Butyrate is a short-chain fatty acid, a molecule often overlooked in the discourse of wellness, yet it is a profound and vital component of our inner ecosystem. While many champion probiotics and fiber, butyrate stands as a testament to the elegant design of the human body, serving as the primary fuel source for the cells lining your colon. This article will elevate your understanding of butyrate, uncovering its vital role in cultivating a thriving gut microbiome and its far-reaching impact on our systemic vitality.
How is Butyrate Produced?
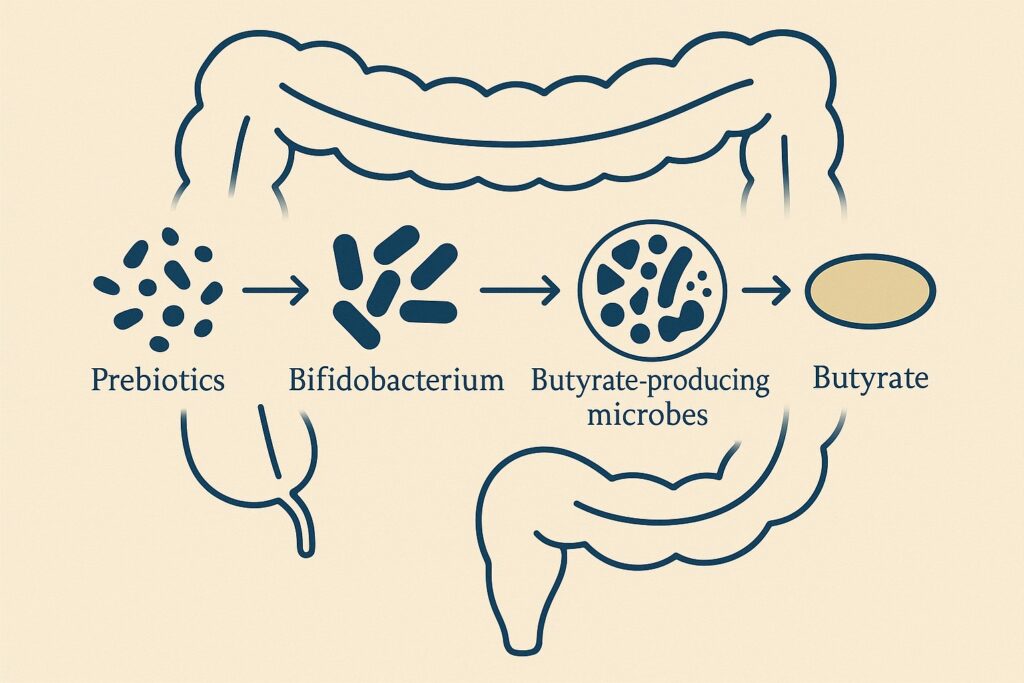
The production of butyrate begins with a partnership between your diet and your biology. When you consume foods rich in dietary fibers, such as those found in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, these fibers travel to the large intestine. There, our beneficial gut bacteria ferment them, producing butyrate alongside other crucial short-chain fatty acids like acetate and propionate. The human gut microbiota produces butyrate through specific biochemical pathways, including the action of enzymes. These pathways are central to the function of the intestinal microbiota in generating butyrate from dietary substrates. This process, a cornerstone of our inherent design, champions the profound synergy between what we consume and our microbial inhabitants..
Butyric Acid and Short Chain Fatty Acids: Understanding the Connection
Butyric acid is one of several short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) produced in the gut, alongside acetate and propionate. These key bacterial metabolites are generated when gut microbiota ferment dietary fiber, resistant starch, and other undigested carbohydrates. While all short-chain fatty acids contribute to gut health, butyric acid stands out for its potent effects on the intestinal tract and beyond. You can read more about other SCFAs and their essential roles in gut and overall health in The Architects of Gut Health: How SCFAs Build Your Foundation for Wellness.
Uncover Advanced Protocols and Launch Access.
For those who champion evidence over hype.
The Biology of Thriving: Butyrate’s Role in Gut Health
Butyrate offers several verifiable benefits that help maintain a healthy gut microbiome. Its efficacy is rooted in precise biological mechanisms that honor the delicate balance of our digestive system.
Supports Colon Health
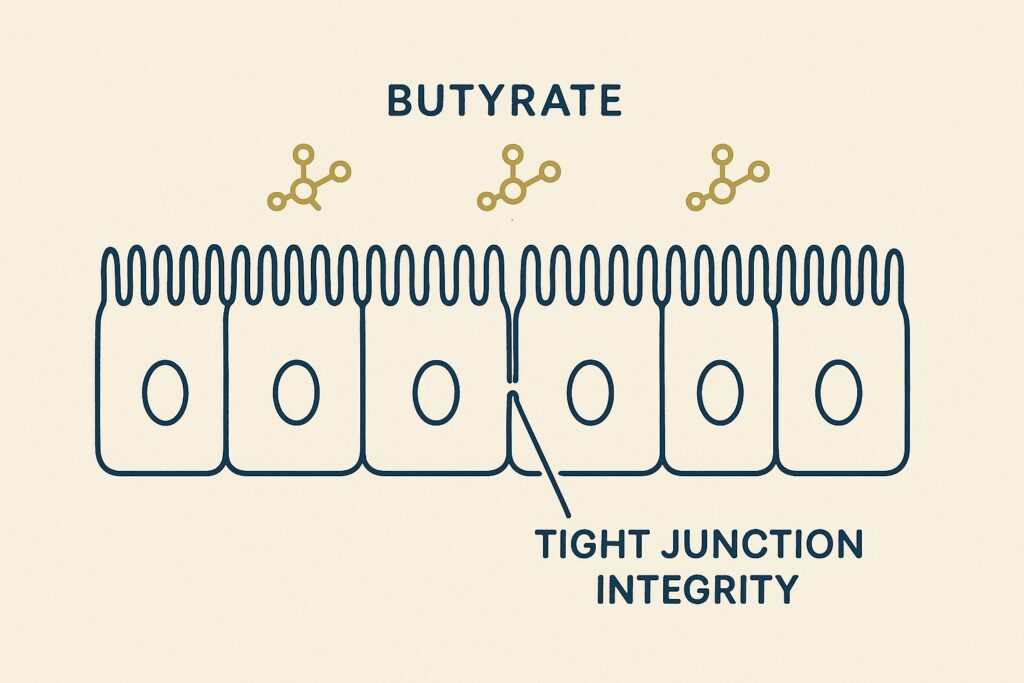
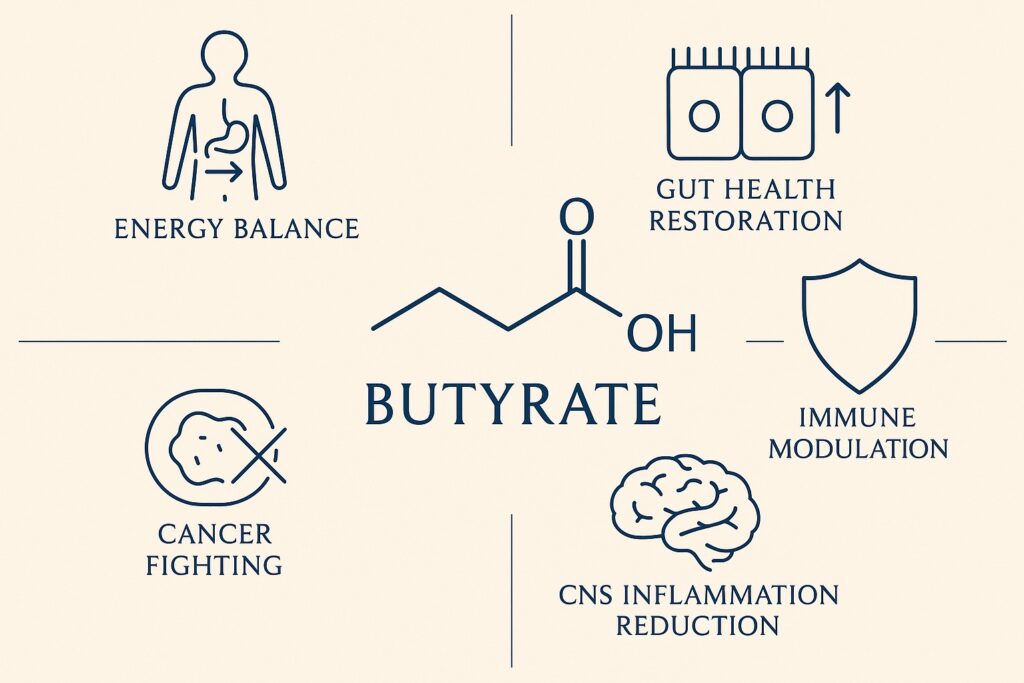
Butyrate is a cornerstone of gut vitality, providing approximately 70% of the energy needs for the cells lining your colon, known as colonocytes [Hamer et al., 2008]. Intestinal butyrate, produced locally in the colon by gut microbiota from dietary fibers, is essential for this energy supply [Liu et al., 2018]. This makes it the primary fuel source for these cells, essential for their function and the structural integrity of your intestinal wall. Butyrate reinforces the intestinal barrier, helping to seal the tight junctions between cells and promoting a strong, protective mucus layer. It also plays a key role in balancing gut immunity, helping to keep the gut environment calm and prevent the body from attacking its own tissues.
Reduces Inflammation
Inflammation in the gut can lead to a variety of health issues, including inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). Butyrate plays a key role in reducing intestinal inflammation by modulating immune responses and cytokine production. Studies have shown butyrate helps reduce inflammation in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) by inhibiting NF-κB, a key protein that activates genes causing inflammation. By blocking NF-κB, butyrate lowers the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and enzymes, and promotes a healthier gut environment. [Recharla et al., 2023].
Promotes a Balanced Gut Microbiome
A diverse and balanced gut microbiome is a prerequisite for holistic health. Butyrate-producing bacteria help cultivate this balance by nourishing the growth of beneficial species while inhibiting the proliferation of harmful ones.This balance contributes to improved digestion, nutrient absorption, and immune function. Research also indicates that butyrate plays a role in regulating immune function and maintaining intestinal homeostasis, all essential components of The Art of Living..
May Prevent Colon Cancer
Researchsuggests that butyrate has potential anti-cancer properties. It may help prevent the development and progression of colon cancer by promoting healthy cell growth and inducing apoptosis—the elegant, programmed cell death in which cancerous cells dismantle themselves. Butyrate can also influence how DNA is organized, helping to silence the genes that drive the growth of cancerous cells. [J.Chen and L.Vietta, 2018]
Butyrate for IBS Management
Butyrate has shown promise in managing symptoms of Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS). A verifiable study from 2013, a double-blind, randomized placebo-controlled trial, involved 66 adults with IBS who received a daily dose of 300 mg of sodium butyrate. The results indicated a significant reduction in abdominal pain and an improvement in overall IBS symptoms compared to the placebo group [Banasiewicz et al., 2013]. This provides verifiable evidence of its efficacy as a therapeutic support.
How to Promote Butyrate Production?
To uncover the full benefits of butyrate, it is essential to support its production from within.
Consume a Fiber-Rich Diet
A diet rich in dietary fibers is key to empowering your microbiome to produce butyrate. Consuming a fiber-rich diet is one of the most effective ways to promote butyrate production in the gut. Include a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, and nuts in your meals. Foods like oats, bananas, and asparagus are particularly beneficial.
Incorporate Prebiotics and Probiotics
Prebiotics are non-digestible fibers that feed beneficial gut bacteria, while probiotics are live bacteria that contribute to a healthy gut microbiome. Healthy gut bacteria play a crucial role in the fermentation process that leads to butyrate formation. Combining both in your diet can enhance butyrate production. Prebiotic-rich foods include garlic, onions, and leeks, while probiotic sources include yogurt, kefir, and fermented vegetables. You can read more about prebiotics and probiotics in (The Science of Postbiotics, Spore Probiotics, and Prebiotics for Optimal Gut Health).
Stay Hydrated
Maintaining good hydration is essential for maintaining a healthy gut environment. Water helps keep the digestive system functioning smoothly, supporting the fermentation process that produces butyrate.
Limit Processed Foods and Sugars
Processed foods and added sugars can negatively impact gut health by promoting the growth of harmful bacteria. Limiting their intake can help maintain a balanced gut microbiome and support butyrate production.
Oral butyrate supplementation is another strategy to support butyrate levels, especially for individuals with low natural production.
Sodium Butyrate Supplements
While dietary sources of butyrate—such as oats, bananas, and asparagus—help nourish gut bacteria, sodium butyrate, or tributyrin supplements provide a more concentrated boost. Tributyrin has higher bioviability and provides slow release. Both supplements can supports gut lining integrity, reduces inflammation, and enhances microbiome balance. It can be particularly beneficial for individuals struggling to produce sufficient butyrate naturally.
The Connection Between Butyrate and Overall Health.
Butyrate’s benefits transcend gut health, impacting various aspects of overall well-being. In addition to supporting digestive function, butyrate provides significant metabolic benefits, including improved energy homeostasis, enhanced lipid metabolism, and increased oxidative metabolism.
Supports Mental Health
The gut-brain axis is a complex communication network between the gut and the brain. As a product of gut bacteria, butyrate can directly affect the brain by crossing the blood-brain barrier or indirectly by stimulating nerves like the vagus nerve. The vagus nerve is like a superhighway that connects your brain to your gut and other organs, carrying messages back and forth. This microbial metabolite can modulate the production and activity of key neurotransmitters, such as glutamate, GABA, dopamine, and serotonin, which play crucial roles in mood, cognition, and behavior. By influencing them and their neural pathways, butyrate helps maintain balance and communication along the gut-brain axis, promoting overall well-being.
Regulates Metabolism
Butyrate has been shown to regulate metabolism by enhancing energy expenditure and reducing fat storage. This can contribute to maintaining a healthy weight and reducing the risk of metabolic disorders such as obesity and type 2 diabetes. Research indicates that butyrate improves insulin sensitivity and increases energy expenditure. [Amiri et al., 2022]
Strengthens Immune Function
A healthy gut microbiome is essential for a robust immune system. Butyrate supports immune function by promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria and reducing inflammation, helping to protect against infections and diseases. Research has shown that butyrate can influence the activity of peripheral blood mononuclear cells, which play a key role in immune regulation and inflammation. Studies have shown that butyrate can regulate immune responses and maintain intestinal stability. [Recharla et al., 2023]
Enhances Cardiovascular Health
Research suggests that butyrate may improve cardiovascular health through several actions like reducing inflammation and improving how the body handles fats and sugars. Butyrate helps in managing cholesterol levels, reducing obesity, and improving how the body uses insulin. Its actions aren’t limited to the gut, and it also impacts other organs and systems to protect the heart and blood vessels. Studies also show butyrate can improve heart tissue damage and protect heart tissue architecture. [Amiri et al., 2022]
Butyrate Supplements: A Meticulous Approach
While dietary sources of butyric acid, such as butter, contain minimal amounts compared to what is produced by your gut, butyrate supplements offer a precise way to elevate levels. There are different forms, with sodium butyrate and tributyrin being the most common. Tributyrin, a “pre-butyrate” compound, is comprised of three butyric acid molecules attached to a glycerol backbone. This intricate structure is theoretically more resistant to breakdown in the upper GI tract, allowing it to be slowly released directly into the colon [La Monica et al., 2025; Roshanravan et al., 2017]
Clinical Safety & Recommended Dosage
A review of existing human studies on butyric acid supplements suggests a favorable safety profile at recommended doses. The 2013 IBS study, for example, reported no significant side effects at a dose of 300 mg per day. However, it’s important to note that the amount of human clinical trial data is limited, and some studies suggest that more than 20 grams per day can be associated with side effects [Cleveland Clinic, 2022], which is why it is critical to consult a healthcare professional to determine a precise, efficacious dosage for your unique needs.

Why Butyrate Deserves a Place in Your Gut Health Routine
Butyrate is a key short-chain fatty acid that supports gut integrity, reduces inflammation, and promotes a balanced microbiome. It may also help uncover defenses against colon cancer. To naturally boost butyrate, prioritize a fiber-rich diet, prebiotics and probiotics, hydration, and limiting processed foods. These habits empower your gut function and overall well-being. By understanding butyrate’s role, you can take meaningful steps towards a healthier, more vibrant life.