When beginning a collagen regimen, one of the most common questions is simple yet important: how long until I actually notice results? Collagen has become one of the most researched and widely used supplements for skin, joints, and connective tissues, but its effects unfold gradually — at the pace of biology, not instant fixes.
Understanding this timeline matters. Collagen peptides don’t work by filling wrinkles or tightening skin overnight; they provide amino acids and bioactive signals that encourage fibroblasts to renew the extracellular matrix and rebuild collagen fibers. These processes take weeks of consistent supplementation to translate into visible improvements.
In this article, we cut through marketing promises to outline what clinical studies really show about collagen’s timeframe. From early shifts in hydration to longer-term changes in elasticity and resilience, here’s the science-backed timeline of what you can expect — and when.
Uncover Advanced Protocols and Launch Access.
For those who champion evidence over hype.

Understanding Collagen
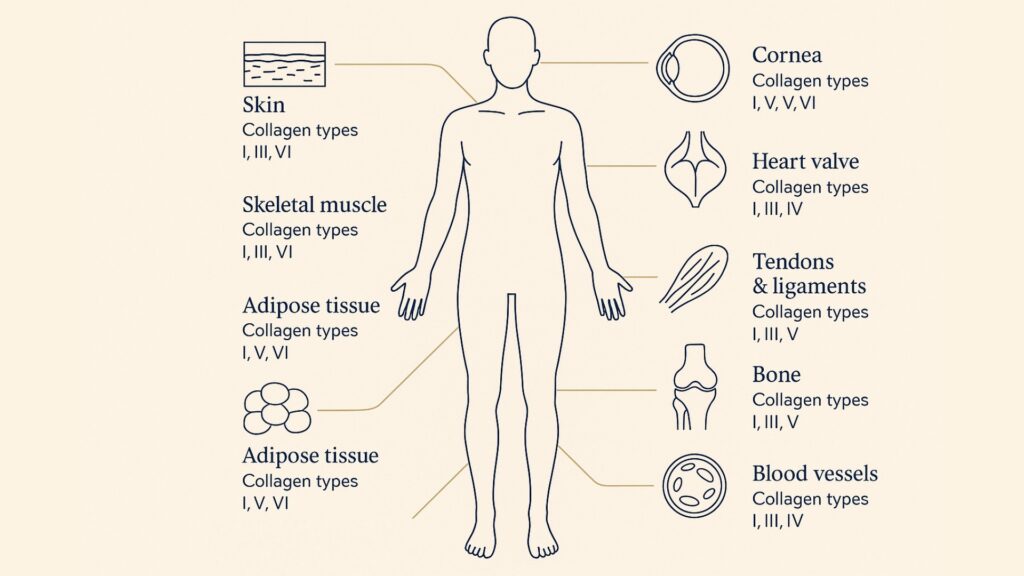
Collagen is the most abundant protein in the human body, making up a significant portion of the body’s total protein content. It acts like the “glue” that holds the body together. It is found in skin, bones, tendons, and connective tissues, where this abundant protein helps provide structure, support, strength, and elasticity. Collagen plays a vital role in maintaining the body’s tissues and overall health.
Type I collagen, the most prevalent, is present in skin and bones. Collagen is also a key component of connective tissue, and certain diseases affecting connective tissue can impact collagen levels and function. As we age, collagen production decreases, resulting in wrinkles and reduced skin elasticity. Additionally, collagen aids in wound healing, bone regeneration, joint health, and dental health.
Collagen Decline as We Age
As we age, our bodies produce less collagen. Our natural production begins a subtle decline from our mid-20s, decreasing by approximately 1-1.5% each year thereafter, This decline leads to lower collagen levels in the body, affecting skin, joints, and connective tissues.
This gradual depletion can accelerate significantly during and after menopause, with some studies suggesting up to 30% of skin collagen can be lost in the first 5 years post-menopause. This period is often marked by a significant reduction in collagen production, making it especially important to address collagen loss during these years.
This natural change contributes to visible signs like wrinkles, reduced skin firmness, and changes in joint comfort. Understanding this process highlights why consciously supporting our body’s collagen resources becomes increasingly important for maintaining resilience and vitality throughout life.
Are Collagen Supplements Worth It?
To answer that question, let’s briefly recap what studies suggest here, you can read in depth assesment in (Do Collagen Supplements Really Work? A Transparent Look at the Evidence).
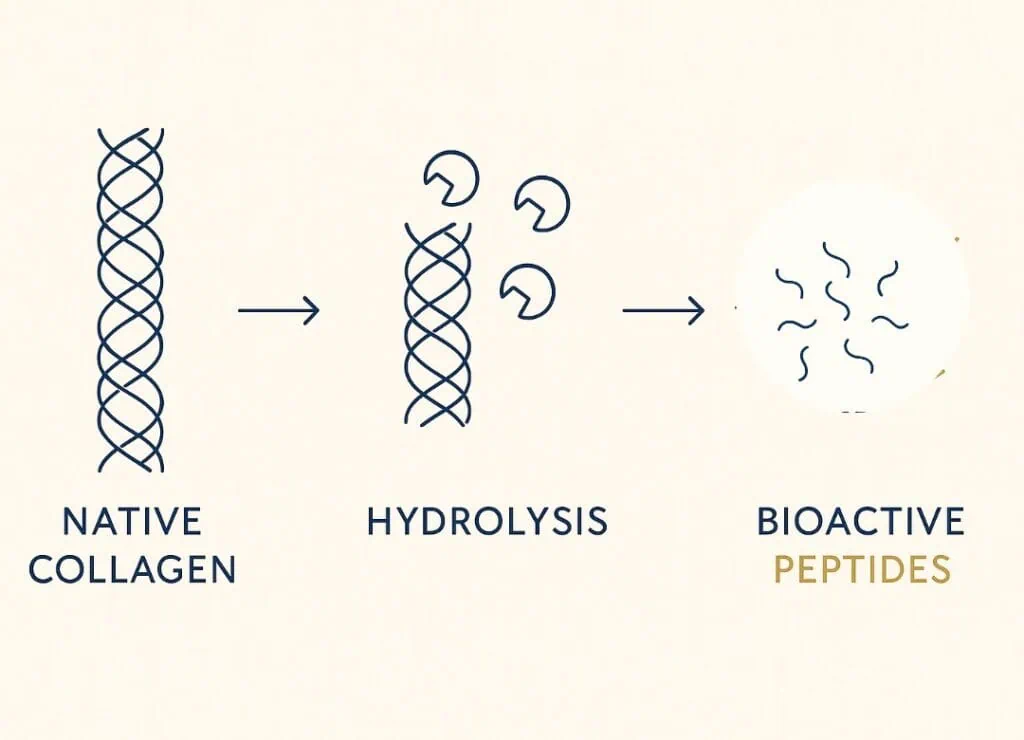
Collagen supplements help the body by providing the building blocks, called amino acids, and bioactive peptides. The body makes collagen by using these amino acids obtained from food and supplements.
These components enter the bloodstream, where the body can utilize them to create new collagen.
- Amino acids are the basic materials.
- Bioactive peptides signal fibroblast cells in the skin to increase collagen production. These peptides also stimulate the production of other important molecules, like hyaluronic acid, which helps with skin hydration. You can read more about (Bioactive Peptides in Collagen Supplements: Benefits, Science, and Choosing the Right One) here.
Collagen cannot be absorbed in its whole form; instead, the body breaks it down into smaller peptides and amino acids before it can be used. The molecular weight of collagen supplements is important because smaller molecules are generally easier for the body to absorb. Hydrolyzed collagen usually has molecular weights between 2,000 Da and 5,000 Da. Researchers often find that lower molecular weights are absorbed more easily.
There are also a number of collagen sources available on the market including animal sources such as bovine and marine collagen, which are popular for their different absorption rates and benefits. You can read more about them and which collagen supplement might be best for you in (Collagen Peptides: UK Guide to Marine vs Bovine Types & Benefits)
What to Expect: Timeline for Noticeable Changes
A Meta-Analyses which assessed the results of many high-quality studies that quantified the effect of taking collagen supplements on the skin, a consistent picture emerges regarding collagen for skin before and after use. Recent reviews looking at numerous trials involving thousands of participants found that taking hydrolyzed collagen peptides regularly leads to noticeable, statistically significant improvements compared to taking a placebo.
These studies included a placebo group to ensure that the observed effects were due to collagen supplementation and not other factors.
You can read more about industry funded vs independent studies in the collagen space and what to look for in (Do Collagen Supplements Really Work? A Transparent Look at the Evidence).
- Improved Skin Hydration: The combined evidence shows collagen users experienced consistently better skin moisture levels than those taking a placebo (pooled SMD ≈ 0.63)
- Enhanced Skin Elasticity: Similarly, the pooled results indicate improvements in the skin’s ability to ‘snap back’ for the collagen groups compared to placebo (pooled SMD ≈ 0.72)
- Reducing Wrinkles: Collagen supplementation was also associated with a reduction in the appearance of wrinkles, a key benefit for those seeking to improve skin appearance.
- The meta-analysis results suggest collagen peptides have a consistent moderate-to-strong positive effect on skin hydration and elasticity compared to placebo – a meaningful and noticeable difference for many. The studies also highlight the potential benefits of collagen supplementation, though individual responses may vary.
How do you translate SMD (Standardized Mean Difference) scores like ≈ 0.63 and ≈ 0.72?
SMD ≈ 0.2 indicates a Small effect size. SMD ≈ 0.5 indicates a Medium or Moderate effect size. SMD ≈ 0.8 indicates a Large effect size.
Timeline
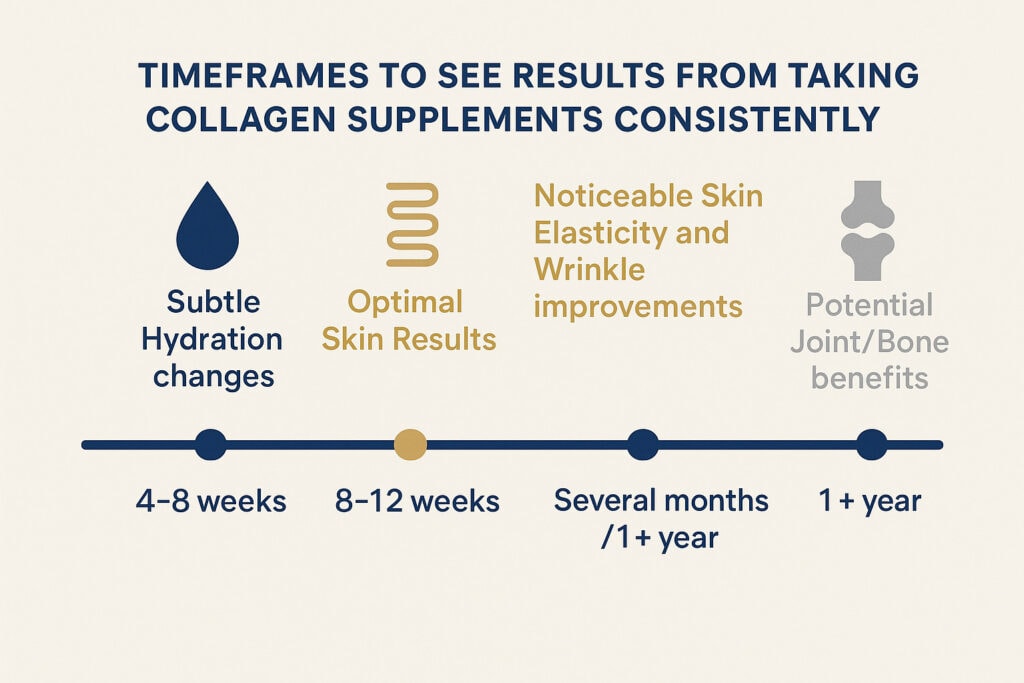
Studies show that the time collagen supplements take to work and show visible results is between 4 to 12 weeks of consistent use. These improvements occur over three stages
- 2 to 4 weeks: Some may notice slight increases in skin hydration.
- 4 to 8 weeks: Skin elasticity improves, with notable hydration changes between weeks 4 and 6.
- 8+ weeks: Significant improvements in hydration and elasticity become apparent. Continued use enhances these effects further.
Collagen works by supporting the skin’s structure at the cellular level, gradually improving hydration and elasticity with consistent, long-term use.
Studies emphasize that hydrolyzed collagen’s benefits become more pronounced after 8 weeks, highlighting the importance of consistency. Collagen supplementation can be especially beneficial for aging skin, helping to improve firmness and elasticity over time.
Individual results can vary due to factors like the type of collagen used, dosage, and frequency of intake. Overall, the benefits of collagen for skin health include improved hydration, elasticity, and a reduction in wrinkles, making it a valuable addition to many skincare routines.
Recommended Duration for Collagen Supplement Use
Collagen supplementation is much like tending to a garden—consistent care and patience yield the best results.
To see real benefits from collagen supplements, it’s best to use them regularly for 3 to 6 months. While some people may notice better skin health and well-being within 4 to 12 weeks, long-term use improves these effects significantly.
How Much Collagen Should You Take?
The recommended daily dosage typically ranges from 2.5 grams to 10 grams of collagen. For more significant improvements in skin hydration or elasticity, consider a dose at the higher end of the range. The amount of collagen needed can vary depending on individual health goals, the type of supplement, and specific formulations, so it’s important to consult a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate intake for your needs.
How to Take Collagen Powder?
- Collagen supplements are commonly available in powder form, making them easy to mix into water, smoothies, yogurt, beverages, or soups.
- Aim for a daily dosage of 5,000 to 10,000 mg.
- Maintain regular intake for at least 3 to 6 months to see noticeable results.
Factors Influencing Collagen Supplements Effectiveness
Individual results from collagen supplements can vary significantly. Factors could include the type of collagen used, the dosage, and the duration of use. Additionally, lifestyle and nutritional choices can impact results.
Maintaining a healthy diet and a balanced diet is essential for supporting collagen production and overall health. Healthy eating provides the necessary amino acids and nutrients required for collagen synthesis. Including collagen rich foods in your meals can help maintain collagen levels naturally. You can also read more about (How to Promote Collagen Production Naturally) here.
It’s also important to consider that certain medical conditions, such as autoimmune diseases—including autoimmune connective tissue diseases like rheumatoid arthritis—can affect collagen production and the effectiveness of supplements.
How Can You Make Collagen Work Faster?
Lifestyle Choices
- Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption significantly hinder collagen production.
- Smoking introduces harmful toxins that reduce blood flow and nutrient delivery to the skin, diminishing collagen synthesis.
- Alcohol dehydrates the skin and disrupts nutrient absorption, further impeding collagen’s ability to maintain skin elasticity and hydration.
UV Radiation
- Sun exposure breaks down collagen fibers and lowers skin quality, accelerating aging signs like wrinkles and fine lines. Thus, protecting your skin while using collagen supplements is essential. To combat UV effects, adopt effective sun protection habits. Use broad-spectrum sunscreen with high SPF, wear protective clothing, and seek shade during peak sun hours.
Nutrients That Support Collagen Production
Collagen synthesis requires several essential vitamins and nutrients that play crucial roles in promoting healthy skin and structure.
- Vitamin C stabilizes collagen fibers.
- Minerals like zinc, iron, and copper are essential for enzymatic processes in collagen production.
- Antioxidants from fruits, vegetables, and nuts help neutralize UV-induced free radicals.
- Biochemical Response: When you’re stressed, your body releases cortisol, a stress hormone that can lead to reduced microbial diversity and an overgrowth of harmful bacteria like Proteobacteria. This imbalance can contribute to inflammatory skin conditions.
- Physical Response: Stress weakens the gut barrier by affecting the tight junctions between epithelial cells, allowing toxins, bacteria, and partially digested food particles to pass into the bloodstream, triggering an immune response.
This inflammatory reaction can further disrupt gut balance and has been linked to anxiety and depression. Stress management techniques such as meditation, yoga, and deep breathing stimulate the vagus nerve, which helps restore the balance of gut bacteria and lowers inflammation.
Long-Term Benefits and Impact on Overall Health
Beyond improving skin, collagen supplementation may contribute to a range of health benefits, including support for, joints, bones and to possibly hair and nails.
Collagen supplements can also aid joint health, reducing joint pain and improving movement by promoting cartilage growth and better joint function. Collagen is a vital component of blood vessels, helping maintain their structure and supporting vascular health for efficient nutrient and oxygen transport throughout the body.
Studies suggest that adding collagen peptides to your diet may enhance bone health, especially for those at risk of osteoporosis or age-related bone loss. The efficacy of collagen supplements is linked to their active ingredients, such as specific collagen peptides, which are absorbed and deliver long-term benefits. Though the timeline for improvement in bone and joint health is longer, you can read more about various studies beyond skin health in (Do Collagen Supplements Really Work? A Transparent Look at the Evidence).
Be first to try our evidence-built formulations.
Collagen Cofactor Complex + Cellular Triad Glutathione Complex.
No noise. No guesswork. Just biologically honest design.
FAQs
Generally, the form of collagen supplement (powder, pills, liquid) has a minimal impact on how quickly it works, as long as the dosage and bioavailability are comparable. Collagen cannot be absorbed in its whole form; it must be broken down into smaller peptides or amino acids for effective absorption. The key factor is how well the collagen has been hydrolyzed (broken down into smaller peptides) for absorption, regardless of the delivery method. Powders are often easier to consume in larger doses, which might lead to perceived faster results for some, but well-formulated pills and liquids can be equally effective if the peptide size and dosage are optimized for absorption.
The first signs that a collagen supplement might be working can vary from person to person. Some individuals report experiencing improved skin hydration within the first few weeks, noticing their skin feels less dry and more supple. Others might observe subtle improvements in nail strength, with less breakage. For joint comfort and other benefits related to deeper tissues, it often takes longer to notice significant changes. Collagen works gradually at the cellular level to improve the strength, appearance of skin with noticeable effects typically developing over weeks to months of consistent use.
To maximise the effectiveness of collagen supplements, it’s advisable to avoid or minimize factors known to hinder natural collagen production and damage existing collagen. These include:
Smoking: Significantly impairs collagen synthesis.- Excessive Alcohol Consumption: Dehydrates the skin and can disrupt nutrient absorption.
Excessive UV Radiation (Sun Exposure): Breaks down collagen fibers. It’s crucial to use sun protection.
High Sugar and Processed Food Intake: Can contribute to inflammation and glycation, damaging collagen.
Nutrient Deficiencies: Ensure you have adequate intake of Vitamin C, zinc, and copper, which are essential for collagen production.
When choosing a supplement, check collagen products for quality, strong formulation with ingrediants that support collagen synthesis, ingredient transparency, and third-party testing. Review the ingredient label for allergens or additives, and consult a healthcare provider if you have concerns.