- Outcomes track dose and peptide MW (lower-MW peptides absorb better).
- Marine vs bovine: no proven winner post-hydrolysis; decide by purity, COA/traceability, dietary fit.
- Evidence: modert to strong for skin; hair/nails low-certainty (Silicon from OSA has clearer hair data than collagen).
The world of wellness is brimming with options, and collagen supplements stand out as a popular choice for those seeking to nurture their vitality from the inside out. Yet, navigating terms like ‘marine’, ‘bovine’, ‘hydrolyzed’, and ‘peptides’ can feel overwhelming when trying to choose the right support for your goals. This guide offers a transparent comparison between the two most common sources – marine and bovine collagen – so you can make an informed choice for your unique health journey.
Marine vs. Bovine Collagen: Which Supplement Source is Right for You?
Both marine and bovine collagen are forms of animal collagen, which are commonly used in supplements..
What is Bovine Collagen?
Bovine collagen is derived from cattle, typically extracted from their hides. High-quality bovine supplements focus on providing primarily Type I and Type III collagen, reflecting the types most abundant in human skin, bones, and connective tissues.
Uncover Advanced Protocols and Launch Access.
For those who champion evidence over hype.
What is Marine Collagen?
Marine collagen comes from fish, usually extracted from their skin and sometimes scales. It is predominantly composed of Type I collagen, making it a popular choice for those focusing specifically on skin benefits.
Bovine: batch COA, amino-acid profile, named supplier, processing facility; raw materials from EU Category 3 hides (low BSE risk; processed per Reg. (EC) 999/2001 & 1069/2009).
Bovine: herd/hide origin + process route; lot/batch traceability (QR acceptable).
Bovine: Halal/Kosher commonly available—verify current certificate.
Bovine: no fish allergen; BSE risk controlled by regulation.
Lower-molecular-weight peptides (≈ ≤ 3 kDa) show stronger bioactivity and fibroblast signalling; post-hydrolysis, purity + MW + dose matter more than species.
Introduction to Collagen
Collagen is the body’s most abundant structural protein—its biological scaffold. It forms the connective tissue matrix that gives skin, bones, and joints their strength and elasticity. Our bodies make collagen naturally from amino acids such as glycine, proline, and hydroxyproline, but this process slows with age, making nutrition and synthesis support increasingly important. For a deeper look at collagen biology, see our dedicated article on collagen synthesis and fibroblast activity.
Why is Collagen Important, Especially As We Age?
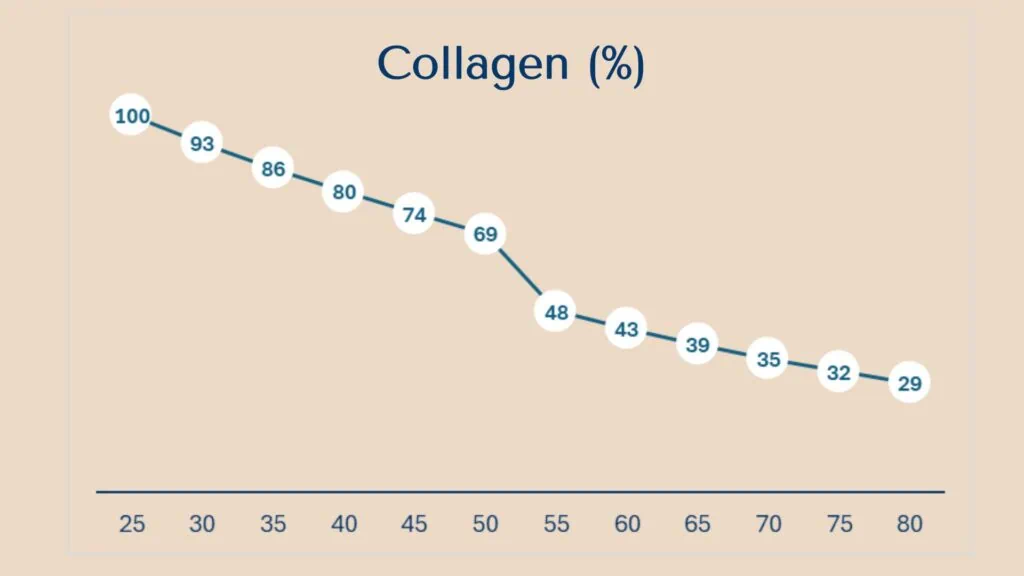
Collagen decline begins quietly in our mid-20s—around 1–1.5 % less each year—and can accelerate after menopause, with up to 30 % of skin collagen lost within the first five years. This reduction weakens skin structure and joint resilience. Supporting collagen renewal during this phase helps maintain elasticity and recovery capacity across tissues. [Skin Collagen Over Lifestages].
What are the Main Types of Collagen in the Body?
Nearly thirty collagen types exist, but three dominate human tissue architecture:
• Type I — ≈ 90 % of body collagen; forms skin, bones, tendons, and ligaments. Provides tensile strength and firmness.
• Type II — Main collagen of cartilage; cushions joints and supports smooth motion.
• Type III — Found alongside Type I in skin and blood vessels; adds elasticity and supports tissue repair. [Skin Collagen through the Lifestages].
Supplement sources mirror these structures: marine collagen provides mainly Type I, while bovine collagen supplies Types I + III for broader structural coverage.
Which Collagen is Better Absorbed? Understanding Hydrolysis & Peptide Size
You’ll often hear that one collagen source — usually fish — is “better absorbed” than another. While this can hold true when comparing raw materials (fish skin vs. bovine hide, for example), the distinction largely disappears in hydrolysed collagen supplements.
Once collagen is enzymatically hydrolysed, its origin matters far less than the degree of hydrolysis and resulting peptide size.
Hydrolysed collagen is broken into smaller peptide chains for absorption. Once hydrolysed, the key determinant is molecular weight rather than species.
• Hydrolysis breaks collagen into smaller peptide chains, allowing absorption through the intestinal wall.
• Low molecular weight peptides (≤ 3 kDa) show the highest bioavailability.
• These bioactive peptides then act as signal molecules, stimulating fibroblasts to produce new matrix proteins such as collagen and elastin.
In short, species ≠ destiny once peptide size and dose are matched. What truly determines efficacy is the hydrolysis process and molecular weight profile, not marketing claims about “fish absorption.” [Hydrolysed Collagen – Sources and Applications].
🧠Think of it like building with LEGOs
- Eating collagen-rich food is like getting a large LEGO structure; your body digests/breaks it down and delivers individual LEGO bricks (amino acids). Your body absorbs these well and uses them to build whatever it needs.
- Hydrolyzed supplements aim to deliver small, pre-assembled LEGO sections (collagen peptides) plus potential building instructions (bioactive signals). The smaller these sections (lower molecular weight), the easier they are to transport through the gut wall to where they are needed.
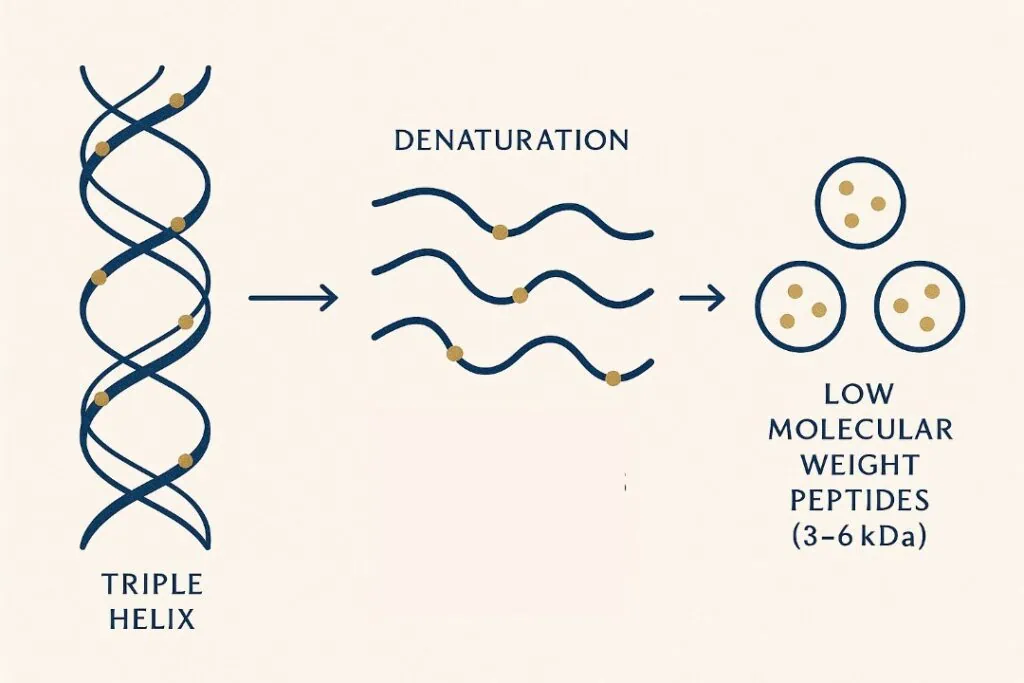
Optimal absorption and potential bioactivity often depend more on effective hydrolysis creating small, easily absorbed peptides (ideally <3kDa) than simply the original animal source itself.
How Do Collagen Peptides Work? The Science of Bioactivity
Collagen peptides don’t simply supply amino acids; they also deliver bioactive fragments that act as cellular messengers. Once absorbed into the bloodstream, these peptides reach the dermis and signal fibroblasts to up-regulate collagen, elastin, and hyaluronic-acid production. This dual action—building blocks + biological signalling—underpins the visible benefits seen in clinical trials
This is a fascinating area of nutritional science, with significant research exploring how different peptides might be used for targeted health support, moving beyond just basic building blocks. You can learn more about these powerful molecules in our dedicated article.
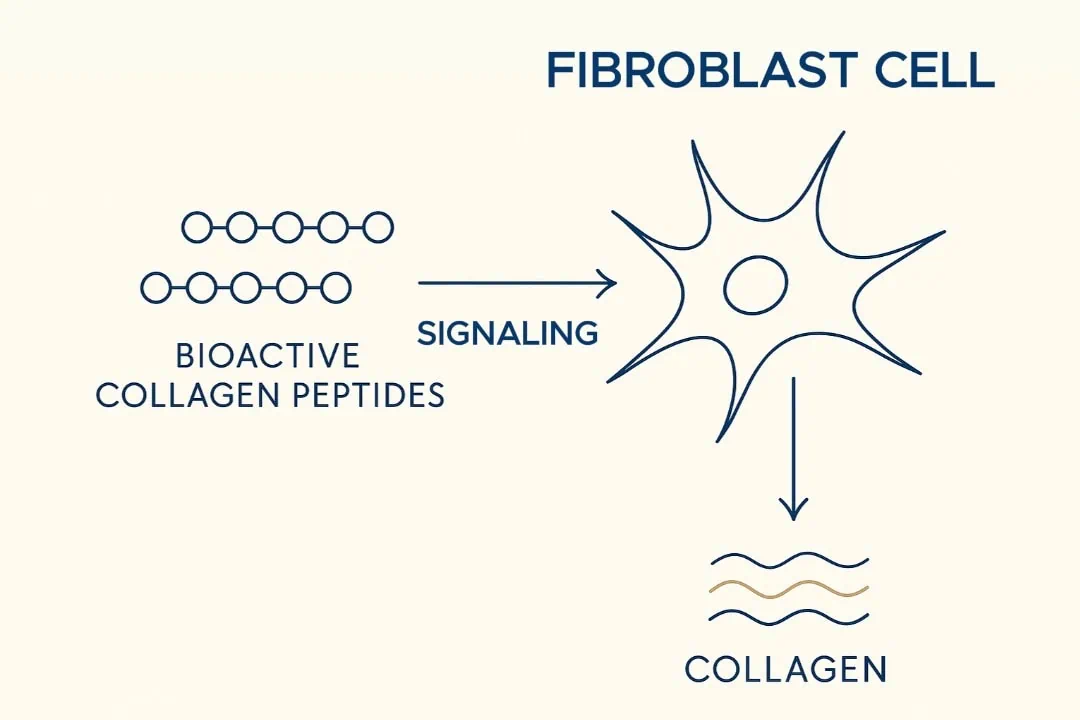
Bioactive peptides act as messengers, prompting fibroblasts to renew the extracellular matrix.
What are the Benefits of Bovine vs Marine Collagen?
To nurture your joints and promote overall well-being during menopause, consider incorporating these scientifically supported supplements and nutrients into your daily routine.
- Marine Collagen (Type I)
Primarily supports structures rich in Type I, like skin, hair, and nails. - Bovine Collagen (Type I & III)
offers broader structural support for skin, muscles, vessels, and joints.
• Both sources deliver bioactive peptides once hydrolysed (< 3 kDa).
• Outcomes depend more on dose (2.5–10 g/day) and duration (8–12 weeks +) than species.
• Across studies, skin hydration and elasticity improve modestly; evidence for hair and nails remains low-certainty.
You can read more about existing and new studies in to the Benefits of Collagen Supplement article.
This approach ensures a more reliable picture than potentially biased single-supplier research. A [2023 meta-analysis] published in the peer-reviewed journal Nutrients, which analyzed data from numerous clinical trials involving over 1700 participants, concluded that oral supplementation with hydrolyzed collagen peptides leads to statistically significant improvements in skin hydration, elasticity, and wrinkles compared to placebo.
These peptides are thought to work not just by providing building blocks, but also by signalling skin cells (fibroblasts) to produce more of their own collagen and other matrix components like hyaluronic acid, supporting skin, joint as well as bone health. You can read in detail about the Benefits of Hydrolysed Collagen, and its Bioactive Peptides functions in our dedicated articles.
Are Bovine and Marine Collagen Halal or Kosher?
Certification checklist:
• Bovine collagen: Halal and Kosher certifications widely available in EU-sourced products — verify certificate number and auditor.
• Marine collagen: Kosher only if fish has fins & scales; Halal requires approved processing aids and traceable source.
• Always check the brand’s published certificate and expiry date on its transparency page.
Vita Katalyst uses COLLinstant® Bovine collagen, which is certified Halal and Kosher, ensuring suitability for individuals following these practices.
Quality means low-molecular-weight peptides (≤ 3 kDa), third-party COA for purity, and transparent sourcing.
How to Choose the Best Collagen Supplement for You?
Many people search for the “best” collagen supplement, but the ideal choice truly depends on your individual needs, goals, and values. Collagen products are classified as dietary supplements and are commonly used to support health, skin, and joints. Instead of seeking one single “best” product, focus on understanding the key quality indicators that contribute to effectiveness and safety. Consider these factors when making your choice:
- Collagen Types: Do you want broad support (Type I & III, common in Bovine) or primarily Type I (common in Marine)? Align the type with your primary goals (e.g., skin, joints, overall).
- Hydrolysis Method & Molecular Weight: As discussed, effective enzymatic hydrolysis yielding low molecular weight peptides (ideally <3kDa) is paramount for bioavailability. Look for brands that specify this.
- Source Reputation & Transparency: Choosing collagen from established manufacturers with expertise provides greater assurance of consistent quality and adherence to safety standards.
- Purity & Testing: High-quality collagen should be purified to remove impurities. Concerns about contaminants like heavy metals can arise with any animal source if not properly controlled. Look for brands that are transparent about their sourcing and utilize suppliers who provide third-party testing data for purity and safety, and verified amino acid content.
- Formulation & Format: Consider if you prefer pure collagen or a formula with added synergistic nutrients. Also think about convenience – supplements come in various formats like large tubs of powder, ready-to-drink liquids, or easy-to-use single-serving sachets.
As with any supplement, there is a potential for adverse effects, and users should be aware of possible risks. It is recommended to consult a health care professional before starting collagen supplementation, especially if you have health conditions or are pregnant.
Marine vs Bovine Collagen: Key Takeaways for Your Choice

When making your choice, consider:
- Both sources yield comparable benefits once hydrolysed and dose-matched.
- Type I dominates skin; Types I + III broaden support to joints and tissue repair.
- Evidence shows modest but real improvements in skin elasticity and hydration.
- Choose based on dietary fit, traceability, and brand transparency — not marketing claims.
Collagen products are classified as food supplements and are intended to complement, not replace, a balanced diet. Taking collagen supplements may offer potential health benefits due to the amino acids and peptides they provide, and whilst there are few studies done into its benefits more research is needed to fully understand their effects. By understanding the science and prioritizing quality processing, you can confidently select a collagen supplement that aligns with your values and supports your journey towards holistic wellness and radiance from within.
Be first to try our evidence-built formulations.
Collagen Cofactor Complex + Cellular Triad Glutathione Complex.
No noise. No guesswork. Just biologically honest design.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Not necessarily. Absorption depends primarily on the molecular weight of the collagen peptides, achieved through hydrolysis. High-quality bovine collagen hydrolyzed to a low molecular weight (<3kDa) can be absorbed just as effectively as similarly processed marine collagen
Both Type I and Type III collagen are crucial for skin health. Type I provides the main structure, while Type III contributes to elasticity and is important in tissue repair. Bovine collagen typically provides both, while marine collagen is primarily Type I. Furthermore, essential vitamins and minerals including Vitamin C, Zinc, and Copper act as necessary co-factors for your body’s own collagen and elastin synthesis. To potentially optimize the effectiveness of supplementation for skin health, consider formulations that also include these supportive nutrients.
Yes, the COLLinstant® Bovine collagen used in Vita Katalyst products is certified Halal and Kosher.
High-quality bovine collagen peptides are generally considered safe with few side effects for most people. As with any supplement, if you have specific health conditions or concerns, it’s always best to consult your healthcare provider. Ensuring the product is sourced reliably and tested for purity minimizes risks.


